Casey C
in progress
- 主成分分析法 (Principal Component Analysis aka PCA):可以减少系统的维数,保留足以描述各数据点特征的信息,其中新生成的维叫做主成分。
The first principal component of the data is the direction in which the data varies the most.
- scikit-learn库里的fit_transform()函数就是用来降维的,属于PCA对象。
- 先导入PCA模块sklearn.decomposition,然后用PCA()构造函数,用n_components选项指定要降到几维,最后用fit_transform()传入参数。
- 以著名的iris数据集为例:
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
x_reduced = PCA(n_components = 3).fit_transform(iris.data)
- 画3D散点图:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
iris = datasets.load_iris()
x = iris.data[:, 1] #X-Axis - petal length
y = iris.data[:, 2] #Y-Axis - petal width
species = iris.target #species
x_reduced = PCA(n_components = 3).fit_transform(iris.data)
#SCATTERPLOT 3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
ax.set_title('Iris Dataset by PCA', size = 14)
ax.scatter(x_reduced[:, 0], x_reduced[:, 1], x_reduced[:. 2], c = species)
ax.set_xlabel('First Eigenvector')
ax.set_ylabel('Second Eigenvector')
ax.set_zlabel('Third Eigenvector')
ax.w_xaxis.set_ticklabels(())
ax.w_yaxis.set_ticklabels(())
ax.w_xaxis.set_ticklabels(())
- 支持向量机(Support Vector Machine,SVM)
指一系列机器学习方法。最基础的任务是判断新观测数据属于两个类别中的哪一个。在学习阶段,这类分类器把训练数据映射到叫作决策空间(decision space)的多维空间,创建叫作决策边界的分离面,把决策空间分为两个区域。可分为SVR(Support Vector Regression,支持向量回归)和SVC(Support Vector Classification,支持向量分类)。
- Standardize vs. Normalize
- Standardize:标准化,一般指正态化,即均值为0,方差为1。一般采用z-score。
- Normalize:归一化,一般指将数据限制在[0,1]之间。一般采用最大-最小规范化对原始数据进行线性变换:X*=(X-Xmin)/(Xmax-Xmin)
- Backpropagation (反向传播算法,BP)
- to calculate the slope for a weight (aka the partial differential of the loss function with regard to the weight):

- to calculate the slope for a weight (aka the partial differential of the loss function with regard to the weight):
- 迭代(iteration):
指重复反馈过程的活动,其目的通常是为了接近并到达所需的目标或结果。每一次对过程的重复被称为一次“迭代”,而每一次迭代得到的结果会被用来作为下一次迭代的初始值。
-
- Validation Dataset: The sample of data used to provide an unbiased evaluation of a model fit on the training dataset while tuning model hyperparameters. The evaluation becomes more biased as skill on the validation dataset is incorporated into the model configuration.
- Test Dataset:
The sample of data used to provide an unbiased evaluation of a final model fit on the training dataset.
The Test dataset provides the gold standard used to evaluate the model. It is only used once a model is completely trained(using the train and validation sets). The test set is generally what is used to evaluate competing models.

- an example
# Import EarlyStopping
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
# Save the number of columns in predictors: n_cols
n_cols = predictors.shape[1]
input_shape = (n_cols,)
# Specify the model
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(100, activation='relu', input_shape = input_shape))
model.add(Dense(100, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(2, activation='softmax'))
# Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss = 'categorical_crossentropy', metrics = ['accuracy'])
# Define early_stopping_monitor
early_stopping_monitor = EarlyStopping(patience = 2)
# Fit the model
model.fit(predictors, target, epochs=30, validation_split= 0.3, callbacks=[early_stopping_monitor])
- Networks
- degree:The degree of a node is the number of neighbors that it has.
- The degree centrality: the number of neighbors divided by all possible neighbors that it could have. Depending on whether self-loops are allowed, the set of possible neighbors a node could have could also include the node itself.
- Betweenness Centrality:一个结点承担最短路桥梁的次数除以所有(最短?)路径数量。It is defined as the fraction of all possible shortest paths between any pair of nodes that pass through the node.
- cliques: cliques are “groups of nodes that are fully connected to one another”.
- maximal clique: a maximal clique is a clique that cannot be extended by adding another node in the graph.
- Supervised learning tips:
Pairwise relationships between continuous variables
We typically want to avoid using variables that have strong correlations with each other – hence avoiding feature redundancy – for a few reasons:
- To keep the model simple and improve interpretability (with many features, we run the risk of overfitting).
- When our datasets are very large, using fewer features can drastically speed up our computation time.
-
Since PCA uses the absolute variance of a feature to rotate the data, a feature with a broader range of values will overpower and bias the algorithm relative to the other features. To avoid this, we must first normalize our data. There are a few methods to do this, but a common way is through standardization, such that all features have a mean = 0 and standard deviation = 1 (the resultant is a z-score).
-
random_state就是为了保证程序每次运行都分割一样的训练集合测试集。否则,同样的算法模型在不同的训练集和测试集上的效果不一样。 当你用sklearn分割完测试集和训练集,确定模型和初始参数以后,你会发现程序每运行一次,都会得到不同的准确率,无法调参。这个时候就是因为没有加random_state。加上以后就可以调参了。
- Bootstrapping: 自助法,bootstrap sampling也称为可重复采样/有放回采样。
- 给定包含m个样本的数据集D,我们对它进行采样产生数据集D’:每次随机从D中挑选一个样本,将其拷贝放入D’,然后再将该样本放回初始数据集D中,使得该样本在下次采样时仍有可能被采到;这个过程重复执行m次后,我们就得到了包含m个样本的数据集D‘。
- 显然,D中有一部分样本会在D’中多次出现,而另一部分样本不出现。

- 自助法在数据集较小、难以有效划分训练/测试集时很有用;然而,自助法产生的数据集改变了初始数据集的分布,这会引入估计偏差。因此,在初始数据量足够时,留出法(hold-out)和交叉验证法(cross-validation)更常用一些。
-
查准率(precision)与查全率(recall):
 F1:基于查准率与查全率的调和平均:
F1:基于查准率与查全率的调和平均:
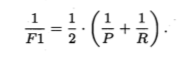

- 调节hyperparemeters可以用GridSearchCV
- Deep Learning Layers:
MaxPooling. This passes a (2, 2) moving window over the image and downscales the image by outputting the maximum value within the window.Conv2D. This adds a third convolutional layer since deeper models, i.e. models with more convolutional layers, are better able to learn features from images.Dropout. This prevents the model from overfitting, i.e. perfectly remembering each image, by randomly setting 25% of the input units to 0 at each update during training.Flatten. As its name suggests, this flattens the output from the convolutional part of the CNN into a one-dimensional feature vector which can be passed into the following fully connected layers.Dense. Fully connected layer where every input is connected to every output.Dropout. Another dropout layer to safeguard against overfitting, this time with a rate of 50%.
- RBM: 受限玻尔兹曼机。A restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) is a generative stochastic artificial neural network that can learn a probability distribution over its set of inputs. Stochastic neural networks are a type of artificial neural networks built by introducing random variations into the network, either by giving the network’s neurons stochastic transfer functions, or by giving them stochastic weights. This makes them useful tools for optimization problems, since the random fluctuations help it escape from local minima.
- GPU
- SVD: singular value decomposition, 奇异值分解。
- HAC: Hierarchical Agglomerative Clustering,层次聚类。
- t-SNE: T-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding, It is a nonlinear dimensionality reduction technique well-suited for embedding high-dimensional data for visualization in a low-dimensional space of two or three dimensions. Specifically, it models each high-dimensional object by a two- or three-dimensional point in such a way that similar objects are modeled by nearby points and dissimilar objects are modeled by distant points with high probability.
-
Flask is super easy and used for a lot of API development in data engineering and for productionizing machine learning models.
-
Start: Pick something you are interested in And solve a problem (Can be soccer betting for all I know)
- Step 1 Learn web scraping using python Will allow you to obtain data on your own, allowing you to analyze any data source you could wish. Learn selenium, requests, beautifulsoup. Learn how to interact with api’s.
- Step 2 Learn how to take said data and create a sql database around it Make multiple trimmed down tables that focus on keeping a certain type of data and can be referenced by other tables to make a master file. I.e. a human database could have A Demographics Table A School History Table A work experience table etc
- Step 3 After creating said database, use said data to create an analysis. Do an analysis of “human” that figures out key components of what makes them successful. ( or whatever your data is about
-
Step 4 Automate data collection, transformation Upload, and analysis
- Bonus Step: Create a web app using node.js / angularjs / Flask (just to throw out a stack this can be done with and keep you from the 50 other options) The web app will show your automated analysis real time, to anyone who wants to see it. Now you will use this project to market yourself. You explain all the things necessary and all the complexities it took to do this project and you’ll be hired in literally no time. You will have shown capability in multiple programming languages, an ability to problem solve and to research, an ability to learn rapidly, and an ability to get things done independently. This last one is very important, can’t tell you how many people need their hands held every step of the way to figure out how to do something. You prove you can do that, you’ll be worth your weight in gold.
- Two trending series may show a strong correlation even if they are completely unrelated. This is referred to as “spurious correlation”. That’s why when you look at the correlation of say, two stocks, you should look at the correlation of their returns/changes and not their levels. ( pct_change())
- Autocorrelation is a mathematical representation of the degree of similarity between a given time series and a lagged version of itself over successive time intervals. It’s the same as calculating the correlation between two different time series, except autocorrelation uses the same time series twice: once in its original form and once lagged one or more time periods.
- Mean Reversion is a theory used in finance that suggest that asset prices and history returns eventually will revert to long-run mean or average level of the entire dataset. This mean can pertain to another relevant average, such as economic growth or the average return of an industry.
- Even if the true autocorrelations were zero at all lags, in a finite sample of returns you won’t see the estimate of autocorrelations exactly zero. In fact, the standard deviation of the sample auto autocorrelation is 1/sqrt(N) where N is the number of observations. Since 95% of a normal curve is between +1.96 and -1.96 standard deviations from the mean, the 95% confidence intervals is ±1.96/sqrt(N). This approximation only holds when the true autocorrelations are all zero. (Autocorrelations at all lags are zero = we cannot forecast future observations based on the past.)
- ADF (augmented Dickey-Fuller test) tests the null hypothesis that a unit root is present in a time series sample.
- Null Hypothesis is a general statement or default position that there is no relationship between two measured phenomena, or no association among groups. It is generally assumed to be true until evidence indicates otherwise. 零假设的内容一般是希望证明其错误的假设。比如说,在相关性检验中,一般会取“两者之间没有关联”作为零假设,而在独立性检验中,一般会取“两者之间有关联”作为零假设。
- p-value is, for a given statistical model, the probability that, when the null hypothesis is true, the statistical summary (such as the absolute value of the sample mean difference between two compared groups) would be greater than or equal to the actual observed results.
- Extract transform load (ETL) is the process of extraction, transformation and loading during database use, but particularly during data storage use. It includes the following sub-processes:
- Retrieving data from external data storage or transmission sources
- Transforming data into an understandable format, where data is typically stored together with an error detection and correction code to meet operational needs
- Transmitting and loading data to the receiving end
- Data warehousing is a technology that aggregates structured data from one or more sources so that it can be compared and analyzed for greater business intelligence. Data warehouses are typically used to correlate broad business data to provide greater executive insight into corporate performance.
- Principles that good ETL pipelines should follow:
- Partition Data Tables
- Load Data Incrementally
- Enforce Idempotency
- Parameterize Workflow
- Add Data Checks Early and Often
- Build Useful Alerts & Monitoring System